Sub-Saharan Africa: Geography, Culture, & Communities Podcast & Study Guide

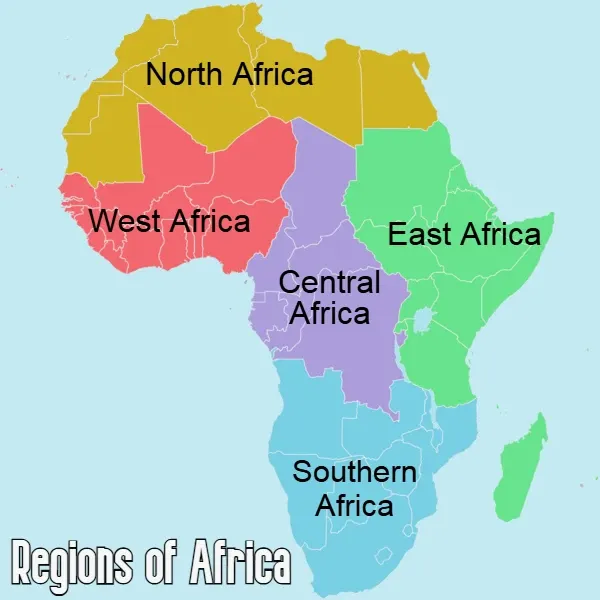
Overview of Sub-Saharan Africa's Regions
West Africa
Region with emerging economies and countries with abundant natural resources like oil and diamonds. Marketplaces are vital for daily life. Music, dance, and oral traditions are deeply rooted in West African culture, with festivals and ceremonies playing a significant role. Challenges include poverty, political instability, and limited access to healthcare and education.
Select Countries include:
- Nigeria: Africa’s most populous country, with a diverse landscape and rich natural resources. It holds significant economic and political influence on the continent, earning it the nickname "Giant of Africa".
- Ghana: The first sub-Saharan African nation to gain independence, symbolizing a gateway to Africa due to its historical and modern roles in connecting the continent to the rest of the world.
- Senegal: Known for its culture and political stability.
- The Gambia: Earned the nickname "The Smiling Coast of Africa" due to its shape resembling a smile and its welcoming people.
- Burkina Faso: Stands out for its commitment to honesty and integrity, reflected in its name meaning “Land of Upright People”.
East Africa
Geographically diverse, including coastal plains, mountains, and the Great Rift Valley. Many countries are known for their wildlife, offering safaris and opportunities for tourism. The region boasts significant landmarks such as Mount Kilimanjaro, Lake Victoria, and Lake Tanganyika. Cultural diversity is evident in the presence of various ethnic groups, languages, and religions. However, some countries grapple with challenges like piracy, political instability, and poverty. Select Countries include:
- Kenya: Famous for wildlife safaris and the Great Rift Valley. Home to the Maasai people.
- Tanzania: Home to Mount Kilimanjaro and renowned for the Serengeti National Park and its wildlife migrations.
- Uganda: Nicknamed the “Pearl of Africa” by Winston Churchill due to its natural beauty and diverse landscapes.
Southern Africa
Known for its striking natural beauty, including deserts, mountains, and coastlines. Rich in resources like diamonds, the region also boasts strong tourism due to its diverse landscapes and wildlife. South Africa stands out as the "Rainbow Nation" due to its cultural diversity. The legacy of apartheid is still felt, and challenges like poaching and income inequality persist. Select Countries include:
- South Africa: Known as the "Rainbow Nation" and the only country with three capital cities. The birthplace of Nelson Mandela and site of the first heart transplant.
- Botswana: Features the Kalahari Desert and has the world’s largest elephant population.
Central Africa
Dominated by the Congo River and Rainforest, this region is one of the most biodiverse in the world. It is home to a variety of indigenous communities and cultures. However, issues such as deforestation, political instability, and poverty hamper development. Select Countries include:
- Cameroon: Nicknamed “Africa in Miniature” because it represents the continent's diverse landscapes, climates, cultures, and wildlife.
- Chad: Referred to as the “Dead Heart of Africa” due to its challenging desert geography.
Key Challenges Across Africa
- Poverty: A persistent problem in many African countries, hindering development and impacting access to necessities.
- Political Instability: Conflict and corruption undermine growth and stability in several nations.
- Poaching: A serious threat to wildlife populations, driven by illegal trade and demand for animal products.
- Climate Change: Impacts water resources, agriculture, and ecosystems, particularly in vulnerable regions like the Sahel
Each region and country possess unique characteristics, strengths, and challenges. While facing issues like poverty, instability, and climate change, African nations also exhibit resilience, cultural richness, and a drive for progress. Understanding these nuances is crucial for informed engagement with the continent and its future.