The Geography of Ancient Rome
Geography is an integral part of the development of ancient civilizations. Rome is one of history's largest and most powerful civilizations. The Roman Empire ruled across parts of three continents (Europe, Africa, and Asia) for over 1,000 years.
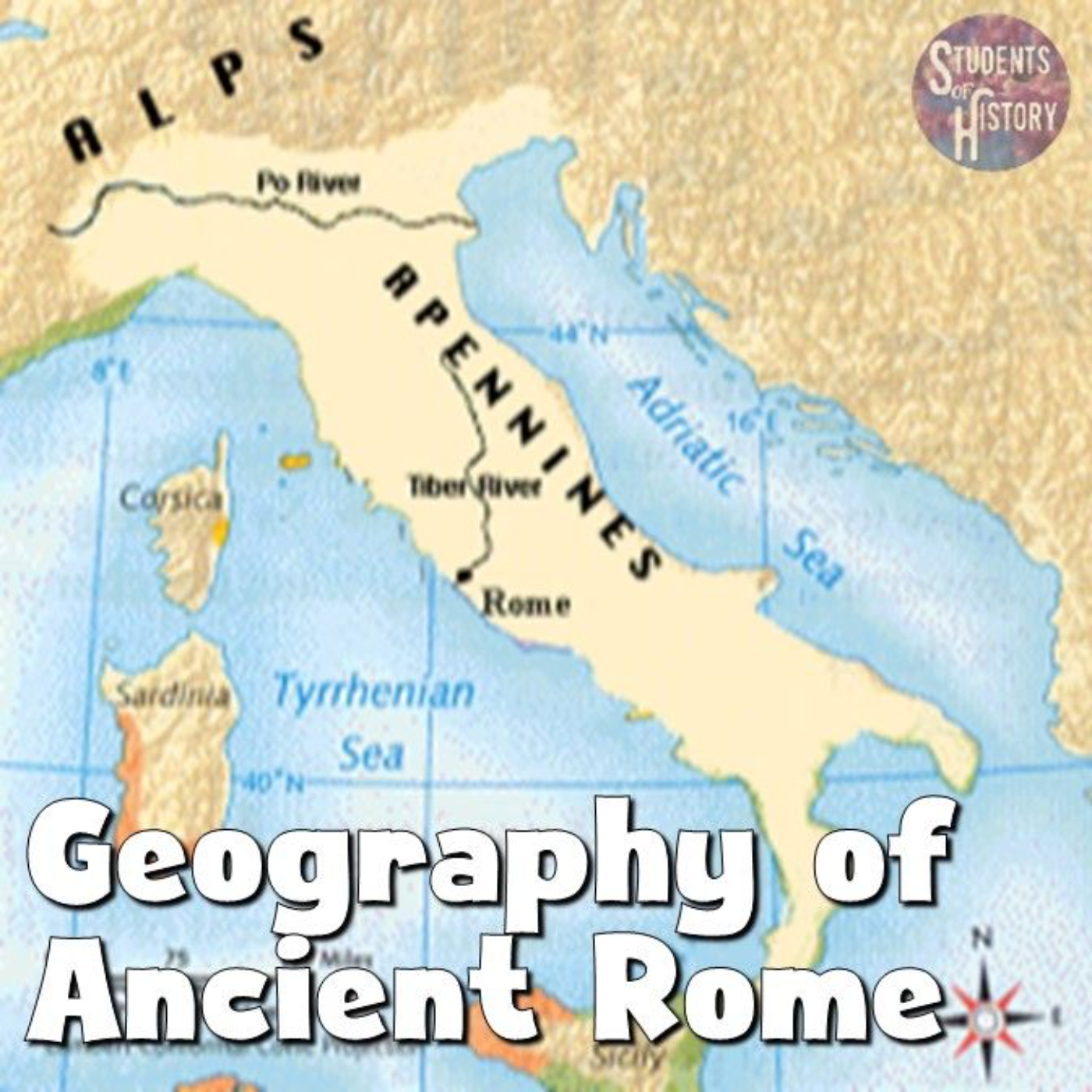
Rome began as a small village near the Tiber River on the Italian Peninsula close to the Mediterranean Sea. The city was far enough inland to provide some protection from those at sea but close enough for ease of transportation.
Several of the region's key geographical features helped Roman civilization to thrive.
The Tiber River is the second longest river in Italy and was a source of freshwater and rich soil needed to support the development of people, animals, and crops of Rome.
The river begins in the Apennine Mountains and flows to the Tyrrhenian Sea, with Rome located to the east of the river.
The Tiber provided easy transportation and the river’s valley created a large area for farming. The river also served as a defense system against attacks coming from the other side of the river.

The Alps and Apennine Mountain ranges were natural barriers that helped protect Rome from invasions and provided a strategic location for the city during war time. The Alps provided a roadblock that forced invaders to move through narrow passages, allowing the Romans time to prepare and attack.
The Apennine Mountains divided the peninsula in half, providing protection against invasion from the east. This allowed Rome to defend against invaders approaching from either side of the mountains.
Covered in forest, the hills and mountains are made of volcanic rock. The Romans used this hard and spongy rock to build the foundations for their structures.
Being close to the Mediterranean Sea allowed Rome to trade with cities in Greece, northern Europe, and North Africa. The Mediterranean also provided the Romans with a rich source of food through fishing.
Inspired by the Phoenicians' skilled shipbuilding, the Romans copied their designs to build their own ships.

They eventually built a navy which assisted them in conquering neighboring territories. Eventually, the Roman Empire took control of all of the Mediterranean Sea's shores.