Regions and Geography
A region is an area that shares common characteristics that distinguish it from the areas around it. Regions are one of the basic units of geography and help us better organize, understand, and explore our world.
Regions can be defined by their physical features, climate, and vegetation or by man-made characteristics like language, culture, or religion.
Purpose of Regions in Geography
Geography uses regions to understand our world. Regions are like puzzle pieces that, when put together, create a vivid picture of an area's diversity.
Dividing the world into regions makes it easier to study different areas. In geography, regions are also important for organization, comparison, planning, and cultural understanding:
Organization: The study of geography is vast and dividing the world into smaller pieces makes it easier to organize and understand. Creating regions allows us to better organize and understand the world systematically.
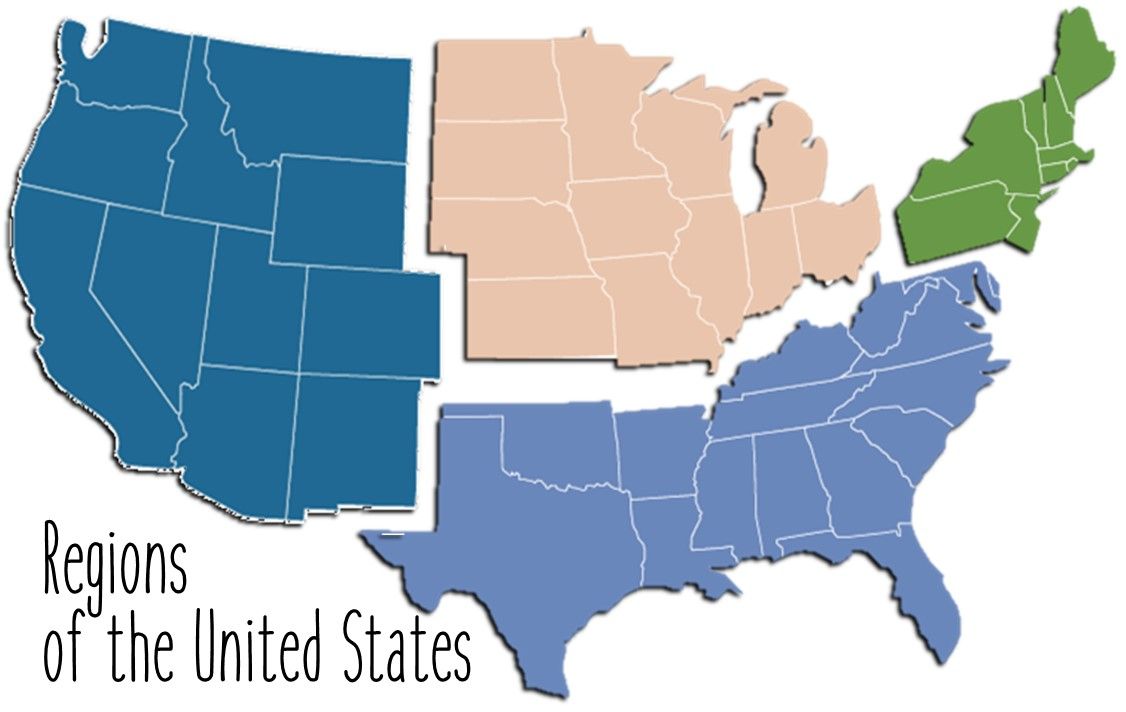
Comparison: Regions give us a framework for comparing different parts of the world. By studying how regions are similar and how they are different in culture, climate, politics, and other areas, we can learn what makes each place unique and how it can relate to other regions.
Planning and Decision-Making: Regions help groups such as businesses, governments, and other organizations make informed decisions. Knowing specific characteristics of a region can help guide strategies for policy, investment, and development for that region. For example, knowing the population of children in a growing area of a city may determine if a new school should be built in that area.
Cultural Understanding: We have always known geography to be about land and water, countries, and even the weather, but it is also about people and culture. Regions are often tied to culture, and by studying them we can learn and get a better understanding about languages, cultures, and lifestyles of different groups of people. This knowledge can help us understand how people can connect in our ever-growing world.
Types of Regions
There are three main categories of regions that geographers use: formal regions, functional regions, and perceptual regions.
Formal Regions
These regions have clear boundaries and specific characteristics that set them apart. These areas are formally recognized with boundaries that everyone can agree upon. These regions could be natural such as an ocean or a forest, or they could be man-made such as a country or state. Europe, the United States, and North America are all formal regions, for example.
Formal regions help us organize and structure our life with the environment and culture of that region. Through the study of formal regions, we can have a better understanding of the cultural, economic, and political landscape of an area and how these aspects interact with other regions around the world.
Functional Regions
These regions are defined by the connections and interactions that are centered around a central point that serves a specific function. That might be a transportation hub like an airport or a school district.
Another example of a functional region is a city or metropolitan area. A city acts as a central point where people from that city and the surrounding areas come together to work, go to school, shop, or socialize with each other.
Functional regions can help us to understand how people are connected in an area, how goods and services are distributed, and how different parts of an area are connected to each other.
Perceptual Regions
These regions are the most flexible as they are based on a person’s feelings, attitudes, or opinions about a place. They can change over time and people might not all agree on where they begin or end.
An example of a perceptual region is Silicon Valley. This region of Northern California contains many of the world’s top tech companies, but it does not have a specific boundary. Other examples are the "good part of town" or the South.
Studying perceptual regions helps us learn how and why people have certain ideas and attitudes about an area and how these regions were created based on culture, language, history, and stereotypes.